How do bitcoin miners get rewarded?
Introduction
Bitcoin miners are not actually solving complex mathematical problems in the traditional sense. Instead, they are performing a process of trial and error to find a specific number (called a nonce) that, when combined with other data from the block, produces a hash value meeting certain criteria.
The reason miners are rewarded for this process is twofold
Network Security and Transaction Validation
Securing the Network
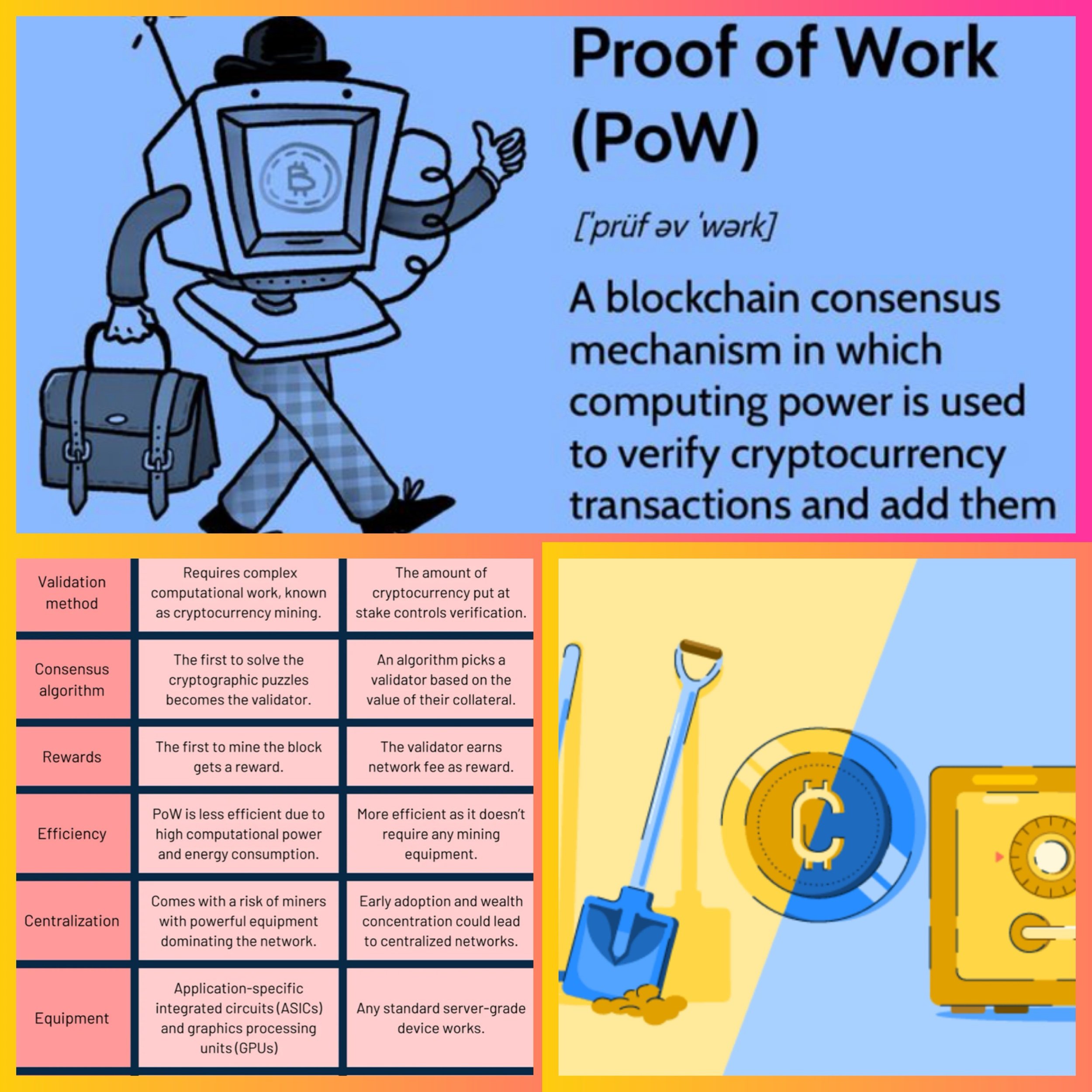
The mining process, known as Proof of Work (PoW), helps secure the Bitcoin network by making it computationally expensive and time-consuming to add new blocks to the blockchain.
Transaction Verification
Miners validate and confirm transactions, ensuring the integrity of the Bitcoin ledger.
Economic Incentives
Block Rewards
Miners receive newly minted bitcoins as a reward for successfully adding a new block to the blockchain. This serves as an incentive for miners to contribute their computational power to the network.
Transaction Fees
In addition to the block reward, miners also receive transaction fees from the transactions included in the block they mine.
Controlled Currency Issuance
The mining reward system serves as the primary method for introducing new bitcoins into circulation. This process helps control Bitcoin’s inflation rate and maintains a predictable supply schedule.
The reward system is designed with a halving mechanism, where the block reward is cut in half approximately every four years. This ensures a gradual and controlled issuance of new bitcoins, with a maximum supply cap of 21 million.
Conclusion
The reward system for Bitcoin mining is not about solving complex mathematical problems, but rather about incentivizing participants to secure the network, validate transactions, and facilitate a controlled issuance of new currency. This system is crucial for maintaining the decentralized nature and security of the Bitcoin network.