How does the proof-of-work mechanism ensure the security of the Bitcoin network
Introduction
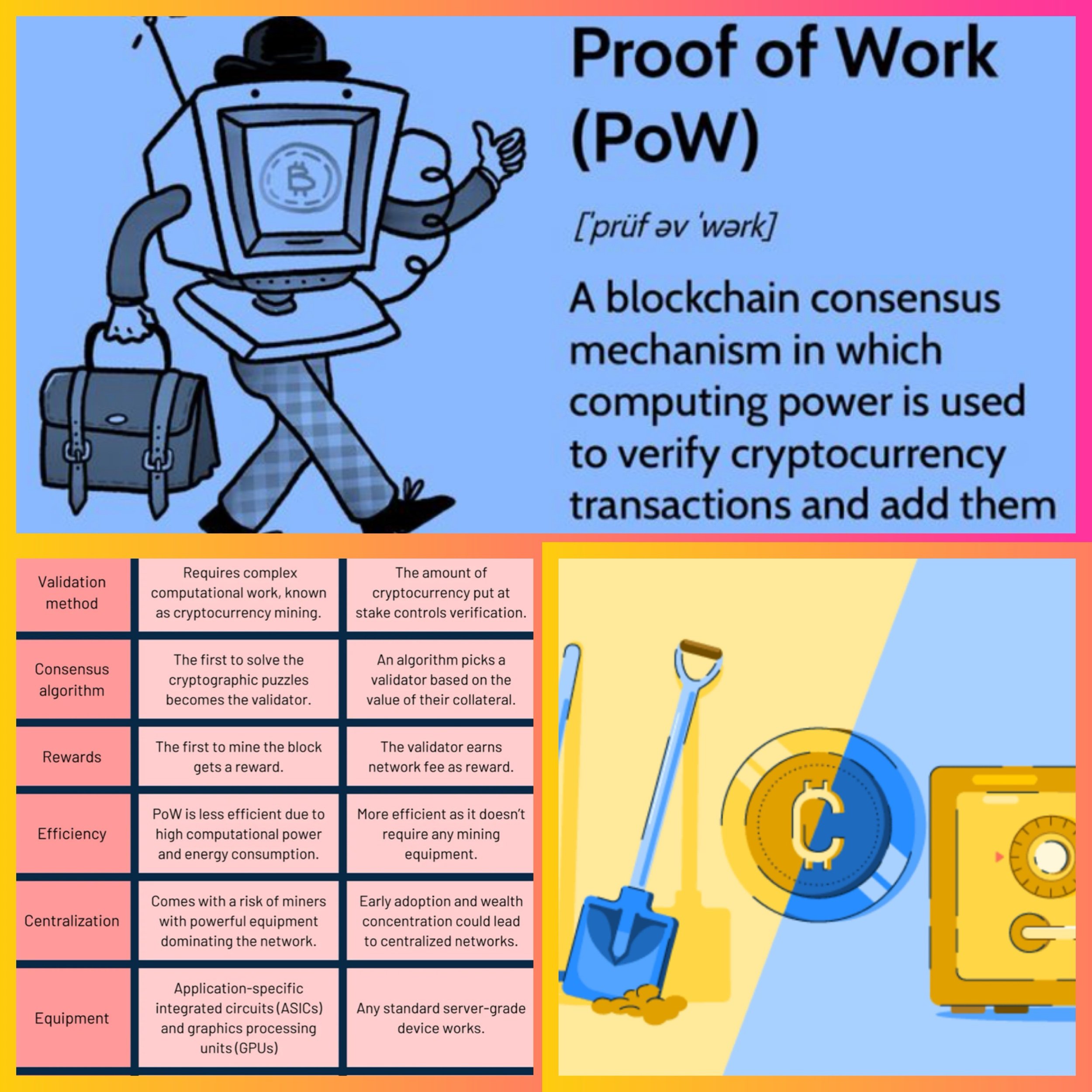
The Bitcoin network first implemented proof of work in 2009, paving the way for other cryptocurrencies. The decentralized nature of PoW allows anyone with the necessary equipment to participate in mining. PoW became the first widely used consensus mechanism to validate cryptocurrency transactions without relying on a third party.
Under PoW, all the computers or nodes in a network compete with each other to solve complex cryptographic puzzles, a process we call cryptocurrency mining. The fastest miner adds new blocks to the blockchain and receives the newly minted digital currency and transaction fees as incentives.
Proof of Work (PoW) in Bitcoin is considered highly secure due to the significant computational power required to validate transactions, making it extremely difficult for malicious actors to manipulate the network and essentially preventing fraudulent activity, thus providing a strong level of security for the Bitcoin blockchain; however, this security comes at the cost of high energy consumption.
Proof of Work (PoW) plays a crucial role in ensuring the security of the Bitcoin network through several key mechanisms.
Decentralization and Consensus
PoW enables a decentralized consensus mechanism, allowing the network to agree on the state of the blockchain without relying on a central authority. This decentralization is achieved by:
Requiring miners to solve complex cryptographic puzzles to validate transactions and add new blocks
Distributing the validation process across a network of independent miners worldwide
Prevention of Double-Spending
PoW helps solve the double-spending problem by:
Making it computationally expensive and time-consuming to alter previously confirmed transactions
Ensuring that the longest chain with the most accumulated work is considered the valid chain, making it extremely difficult for an attacker to create an alternative chain faster than the honest network
Network Security Through Resource Investment
The PoW mechanism secures the network by:
Requiring significant computational power and energy expenditure, making attacks prohibitively expensive
Creating an economic incentive for miners to act honestly, as the cost of attacking the network outweighs potential gains
Immutability and Tamper-Resistance
PoW contributes to the immutability of the Bitcoin blockchain by:
Making it computationally infeasible to alter past transactions without redoing all the subsequent proof of work
Ensuring that as more blocks are added to the chain, the security of older transactions increases exponentially
Protection Against Various Attacks
The PoW consensus mechanism helps protect the Bitcoin network from several types of attacks:
51% attacks: While theoretically possible, the enormous computational power required makes such attacks economically unfeasible
Sybil attacks: The resource-intensive nature of PoW prevents a single entity from easily creating multiple identities to overwhelm the network
Incentive Alignment
PoW aligns the incentives of network participants by:
Rewarding miners with newly minted bitcoins and transaction fees for their honest participation
Encouraging miners to validate only legitimate transactions to maintain the network’s integrity and value
Conclusion
The proof-of-work mechanism ensures the security of the Bitcoin network by creating a system that is decentralized, resistant to tampering, and economically incentivized to maintain its integrity. This combination of technical and economic factors makes Bitcoin’s blockchain one of the most secure and reliable distributed systems in existence.