What is proof of work for dummies
Introduction
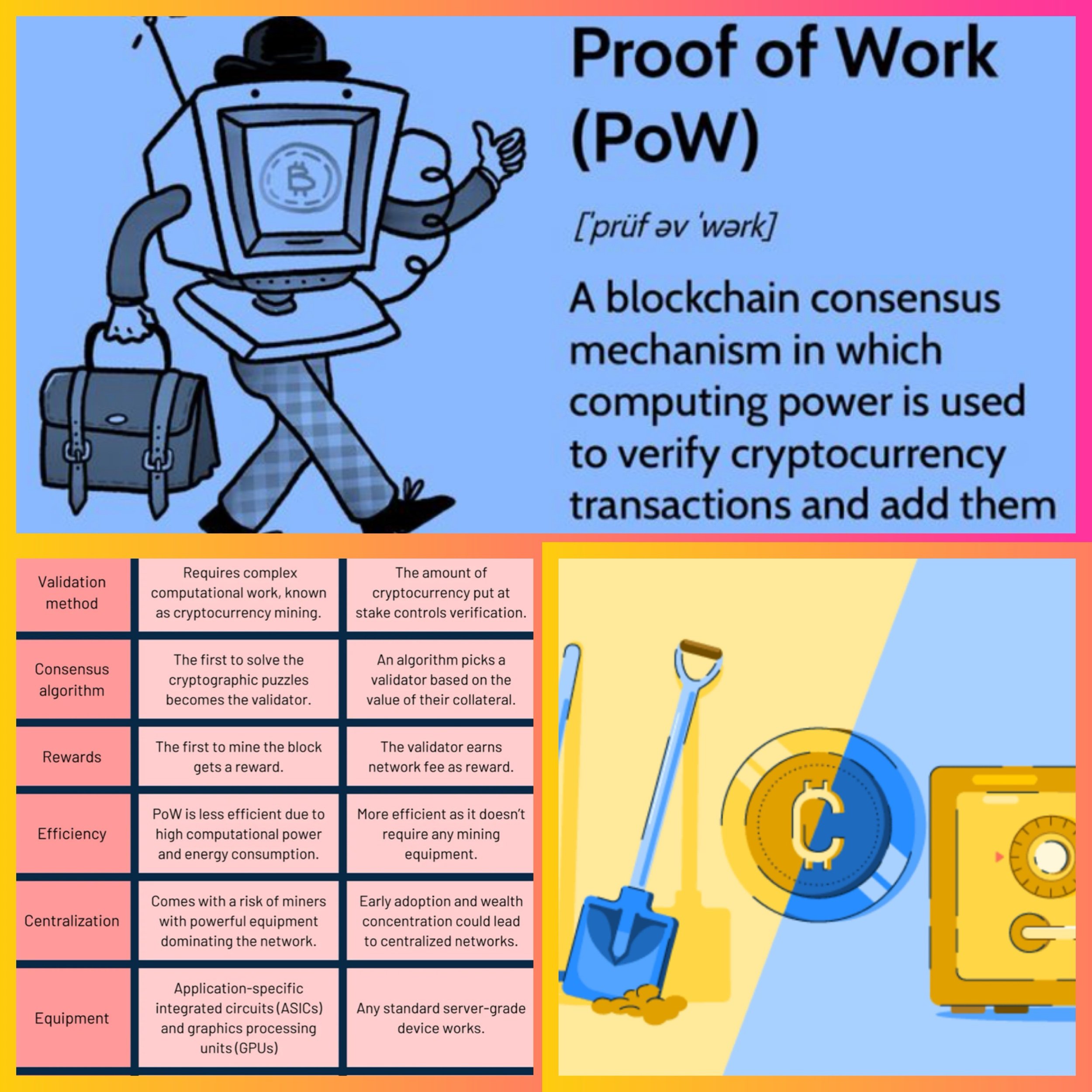
Proof of Work (PoW)
in Bitcoin is a consensus mechanism used to validate transactions and add them to the blockchain.
Here's a concise explanation
Mining
Miners compete to solve complex mathematical puzzles. These puzzles require significant computational power.
Puzzle Solving
The puzzle involves finding a hash below a certain target (determined by the network's difficulty adjustment). This hash is created from combining transaction data, the previous block's hash, and a nonce (number used once).
Validation
Once a miner finds a valid solution, they broadcast it to the network. Other nodes verify the solution. If valid, the block of transactions is added to the blockchain.
Reward
The miner who solves the puzzle first earns newly minted bitcoins (block reward) and transaction fees from the transactions included in the block.
Security
PoW makes it computationally expensive to tamper with the blockchain because altering any single block would require re-mining it and all subsequent blocks, deterring malicious activities due to the high energy and computational cost.
Difficulty Adjustment
Bitcoin adjusts the difficulty of these puzzles approximately every two weeks (or every 2016 blocks) to ensure blocks are added approximately every 10 minutes, regardless of changes in the total mining power on the network.
Conclusion
This system ensures that adding new blocks to the blockchain is decentralized, secure, and maintains the integrity of the transaction history.