What is Bitcoin for Dummies
Introduction
Bitcoin is a decentralized digital currency and payment system that operates without the need for intermediaries like banks or governments.
Created in 2008 by an anonymous person or group using the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto, Bitcoin was designed to enable secure peer-to-peer transactions over the internet.
Key Features of Bitcoin
Decentralization: Bitcoin operates on a distributed network of computers, with no central authority controlling it.
Limited Supply
There will only ever be 21 million bitcoins in existence, making it a potentially deflationary asset.
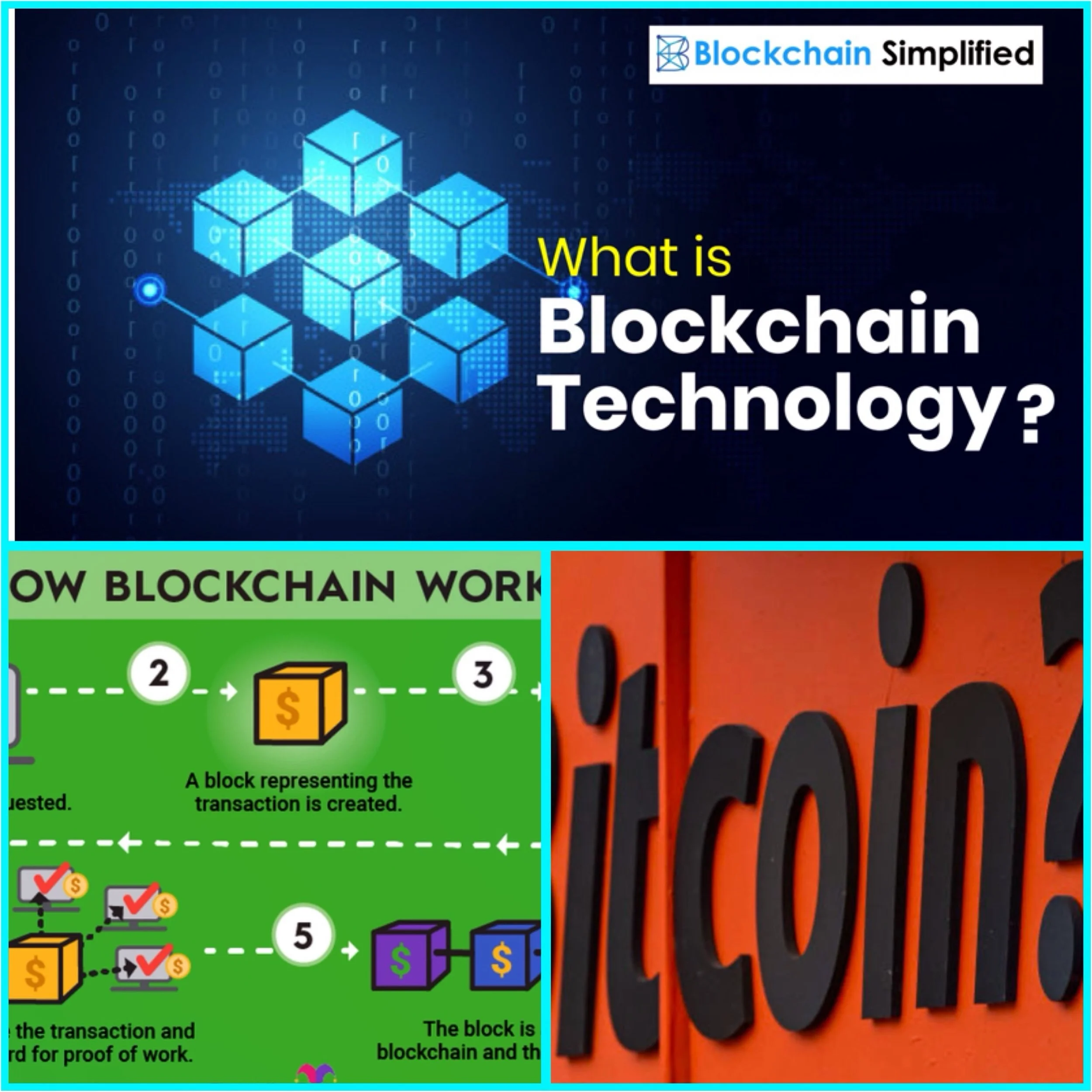
Blockchain Technology
Bitcoin transactions are recorded on a public ledger called the blockchain, which is maintained by a network of computers around the world.
Cryptography
The system uses advanced cryptographic techniques to secure transactions and control the creation of new bitcoins.
How Bitcoin Works
Transactions
Users can send bitcoins directly to each other through a peer-to-peer network.
Mining
New bitcoins are created through a process called mining, where powerful computers solve complex mathematical problems to validate transactions and add them to the blockchain.
Wallets
Bitcoin is stored in digital wallets, which contain public and private keys used to initiate and sign transactions.
Blockchain
All transactions are recorded on the blockchain, creating a permanent and transparent history of all Bitcoin activity.
Uses of Bitcoin
Store of Value
Some people view Bitcoin as a digital alternative to gold, potentially serving as a hedge against inflation.
Medium of Exchange
Bitcoin can be used to purchase goods and services from businesses that accept it as payment.
Investment
Many individuals and institutions buy Bitcoin as a speculative investment, hoping its value will increase over time.
Conclusion
While Bitcoin has gained significant popularity and value since its inception, it’s important to note that it remains a volatile asset with potential risks, including price fluctuations, regulatory challenges, and security concerns.