Alawities clash in Latakia now?
Introduction
Recent clashes between pro-Assad militias and Syrian security forces in Latakia mark the latest violent challenge to the new government’s authority in Syria.
The incident, which resulted in fatalities on both sides, highlights the ongoing tensions and instability in the country following the ousting of Bashar al-Assad’s regime in December 2024.
Background
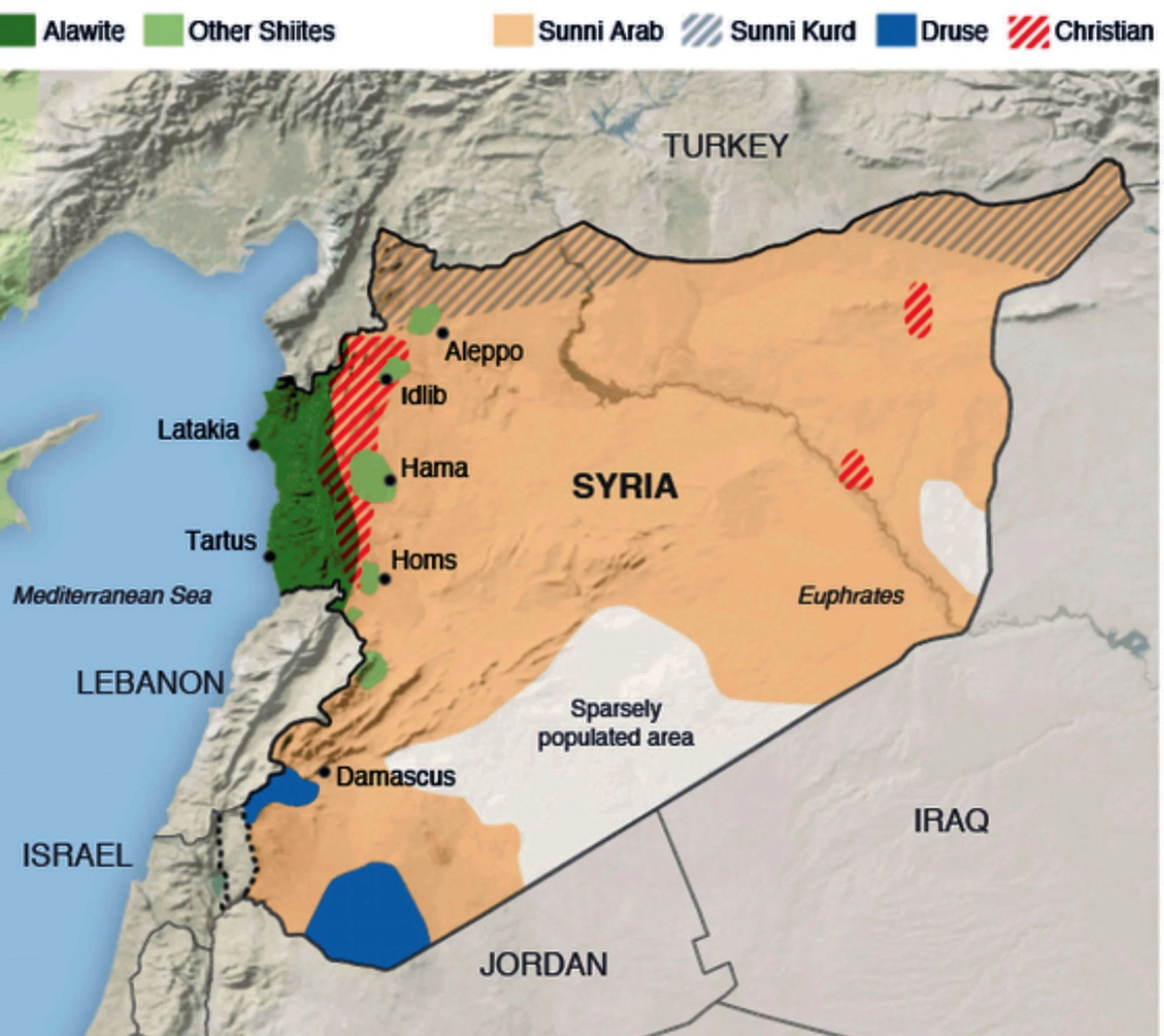
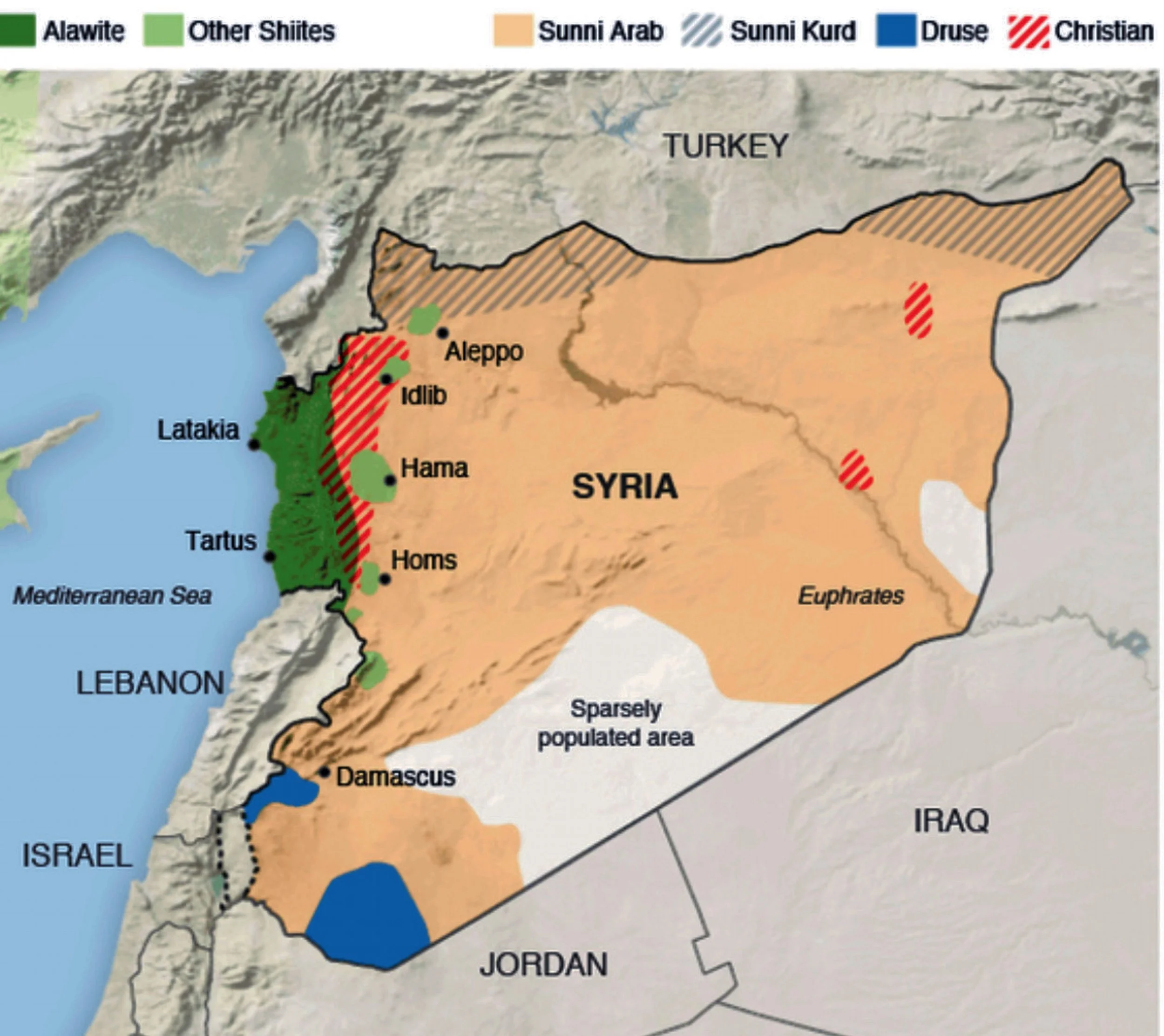
The cities of Latakia and Tartusin Syria are predominantly Alawite. Other cities and regions with a large Alawite population include Homs, Hama, and Damascus.
On December 8, 2024, opposition forces led by the Islamist group Hayat Tahrir al-Sham (HTS) captured Damascus, ending the Assad family’s five-decade rule in Syria. Since then, the new authorities have faced the monumental task of stabilizing the country and addressing sectarian tensions.
Recent Clashes
The most recent violent confrontation occurred in Latakia, a coastal province known as an Assad stronghold:
Two members of the transitional security forces were killed in the clash with pro-Assad militias.
This incident follows a more severe clash in neighboring Tartous province on December 26, 2024, where 14 security personnel were killed in an ambush by Assad loyalists.
Ongoing Challenges
The new Syrian government faces several challenges in consolidating control:
Remnants of Assad’s regime
Security forces are actively pursuing former regime members and loyalists who continue to resist the new authorities.
Sectarian tensions
Protests have erupted in various cities, particularly in Alawite-majority areas, over perceived threats to minority communities.
Balancing act
The new leadership must address calls for accountability for past regime abuses while also preventing revenge killings and maintaining stability.
International recognition
The new government is seeking to establish ties with various countries while managing the complex geopolitical landscape left by Assad’s fall.
Government Response
The transitional authorities have taken several steps to address these challenges:
Launching security operations against pro-Assad militias in former regime strongholds.
Imposing curfews and increasing security presence in areas of unrest.
Pledging to protect minority rights and ensure justice for victims of the former regime.
Banning the publication of sectarian content that could incite division.
Conclusion
As Syria’s new rulers continue to grapple with these complex issues, the situation remains volatile. The coming months will be crucial in determining whether the country can achieve stability and reconciliation after years of brutal civil war.
What we are seeing in Syria is begining of a new regional civil war. Alawites who are 12 % population are backed by Iran. They will become rebels. Syrian government is Sunni and Alawite are a sect of Shia’s.
Another big issue is SDF and ISIS. The worst is Turkey trying to destabilize Syria. There are other minorities in Syria.
What a dangerous place for minorities and how will development efforts start. They need $400 million to rebuild Syria with all these elements struggling with each other for power.